Understanding binomial coefficient and conditional probability with R script
1. Binomial coefficient and probability
(1) Using choose( ) to calculate a binomial coefficient
choose(10, 2) # the number of sets with 2 elements that can be chosen from a set with 10 elements.
## [1] 45
choose(45, 6) # the number of sets with 6 elements that can be chosen from a set with 45 elements.
## [1] 8145060
(2) The binomial coefficient of Lottery 6/45
choose(45, 6)
## [1] 8145060
(3) The probability of winning the first prize in Lottery 6/45
1 / choose(45, 6)
## [1] 1.227738e-07
(4) The probability of winning the fifth prize in Lottery 6/45
choose(6, 3)*choose(39, 3) # picking three from winning numbers and the other three from the rest
## [1] 182780
choose(6, 3)*choose(39, 3) / choose(45, 6)
## [1] 0.0224406
2. Calculating conditional probability using logical operators
(1) Making a set(n=10) of English and math scores
SCORES = data.frame(
english_score= c(60,70,74,78,80,83,85,90,95,100),
math_score = c(75,70,60,85,100,84,94,70,90,92))
SCORES
## english_score math_score
## 1 60 75
## 2 70 70
## 3 74 60
## 4 78 85
## 5 80 100
## 6 83 84
## 7 85 94
## 8 90 70
## 9 95 90
## 10 100 92
(2) Selecting an interest variable from the data
SCORES$english_score
## [1] 60 70 74 78 80 83 85 90 95 100
(3) Applying logical operators to see if each observation satisfies the condition
SCORES$english_score>=90
## [1] FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE TRUE
(4) Counting the number of observations satisfying the condition
sum(SCORES$english_score>=90)
## [1] 3
(5) Using mean( ), calculating the conditional probability
mean(SCORES$english_score>=90)
## [1] 0.3
mean(SCORES$math_score>=90)
## [1] 0.4
(6) Using &, calculating the probability that satisfying both two conditions
mean(SCORES$english_score>=90 & SCORES$math_score>=90)
## [1] 0.2
(7) Using |, calculating the probability that satisfying one of the two conditions
mean(SCORES$english_score>=90 | SCORES$math_score>=90)
## [1] 0.5
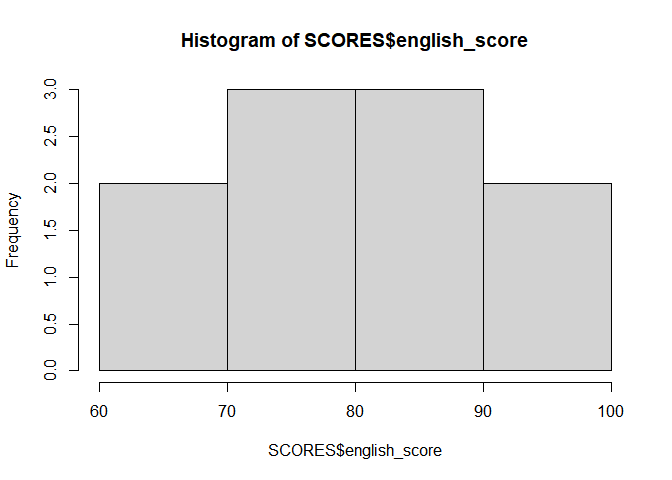
(8) Making a histogram of one variable
hist(SCORES$english_score)
hist(SCORES$english_score, probability=TRUE)
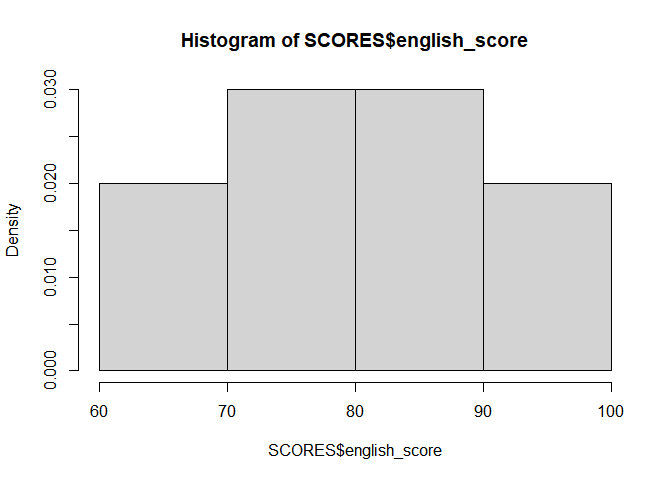
## Changing y-axis into density
3. Calculating conditional probability using subset( )
(1) Making a scatterplot with two variables
plot(SCORES$english_score, SCORES$math_score, pch=16)
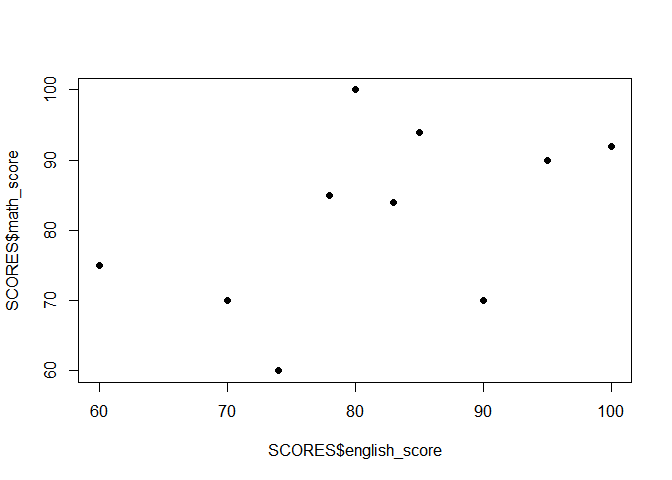
(2) Using subset( ), making subsets
MATH_GOOD = subset(SCORES, math_score>=80)
MATH_GOOD
## english_score math_score
## 4 78 85
## 5 80 100
## 6 83 84
## 7 85 94
## 9 95 90
## 10 100 92
MATH_BAD = subset(SCORES, math_score<80)
MATH_BAD
## english_score math_score
## 1 60 75
## 2 70 70
## 3 74 60
## 8 90 70
(3) Calculating conditional probability from the subsets
mean(MATH_GOOD$english_score>=90)
## [1] 0.3333333
mean(MATH_BAD$english_score>=90)
## [1] 0.25
